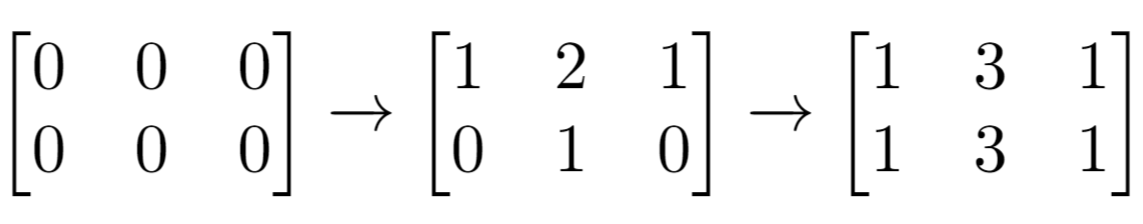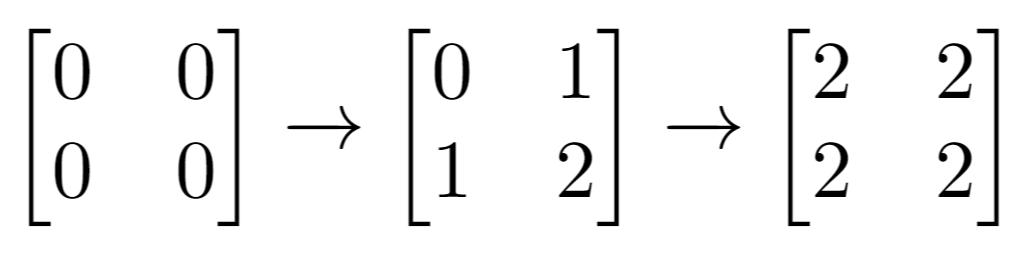题目描述
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵,最开始的时候,每个单元格中的值都是 0。
另有一个二维索引数组 indices,indices[i] = [ri, ci] 指向矩阵中的某个位置,其中 ri 和 ci 分别表示指定的行和列(从 0 开始编号)。
对 indices[i] 所指向的每个位置,应同时执行下述增量操作:
ri 行上的所有单元格,加 1 。ci 列上的所有单元格,加 1 。
给你 m、n 和 indices 。请你在执行完所有 indices 指定的增量操作后,返回矩阵中 奇数值单元格 的数目。
示例 1:
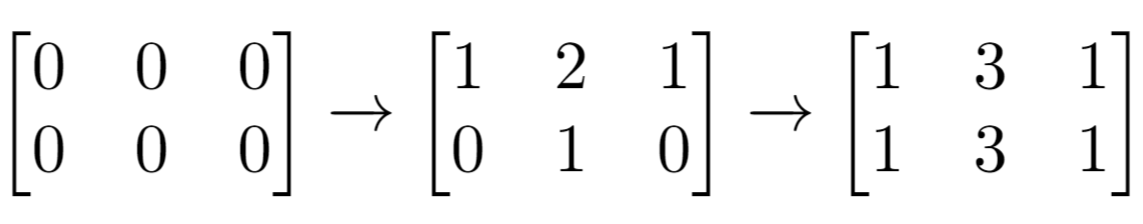
输入:m = 2, n = 3, indices = [[0,1],[1,1]]
输出:6
解释:最开始的矩阵是 [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]。
第一次增量操作后得到 [[1,2,1],[0,1,0]]。
最后的矩阵是 [[1,3,1],[1,3,1]],里面有 6 个奇数。
示例 2:
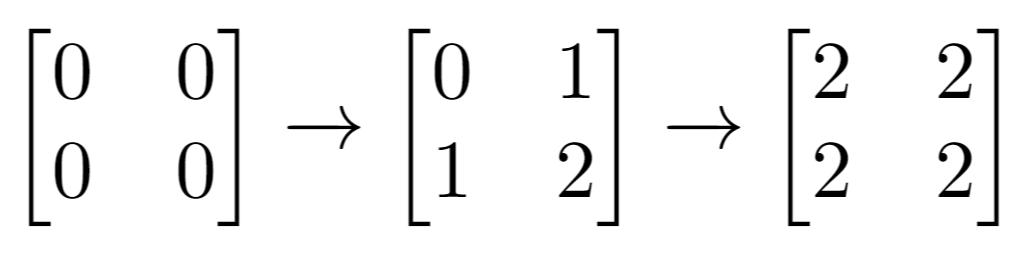
输入:m = 2, n = 2, indices = [[1,1],[0,0]]
输出:0
解释:最后的矩阵是 [[2,2],[2,2]],里面没有奇数。
提示:
1 <= m, n <= 501 <= indices.length <= 1000 <= ri < m0 <= ci < n
进阶:你可以设计一个时间复杂度为 O(n + m + indices.length) 且仅用 O(n + m) 额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?
解法
方法一:模拟
我们创建一个矩阵 \(g\) 来存放操作的结果。对于 \(\textit{indices}\) 中的每一对 \((r_i, c_i)\),我们将矩阵第 \(r_i\) 行的所有数加 \(1\),第 \(c_i\) 列的所有元素加 \(1\)。
模拟结束后,遍历矩阵,统计奇数的个数。
时间复杂度 \(O(k \times (m + n) + m \times n)\),空间复杂度 \(O(m \times n)\)。其中 \(k\) 为 \(\textit{indices}\) 的长度。
| class Solution:
def oddCells(self, m: int, n: int, indices: List[List[int]]) -> int:
g = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
for r, c in indices:
for i in range(m):
g[i][c] += 1
for j in range(n):
g[r][j] += 1
return sum(v % 2 for row in g for v in row)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 | class Solution {
public int oddCells(int m, int n, int[][] indices) {
int[][] g = new int[m][n];
for (int[] e : indices) {
int r = e[0], c = e[1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
g[i][c]++;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
g[r][j]++;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int[] row : g) {
for (int v : row) {
ans += v % 2;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 | class Solution {
public:
int oddCells(int m, int n, vector<vector<int>>& indices) {
vector<vector<int>> g(m, vector<int>(n));
for (auto& e : indices) {
int r = e[0], c = e[1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
++g[i][c];
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
++g[r][j];
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (auto& row : g) {
for (int v : row) {
ans += v % 2;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 | func oddCells(m int, n int, indices [][]int) int {
g := make([][]int, m)
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]int, n)
}
for _, e := range indices {
r, c := e[0], e[1]
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
g[i][c]++
}
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
g[r][j]++
}
}
ans := 0
for _, row := range g {
for _, v := range row {
ans += v % 2
}
}
return ans
}
|
方法二:空间优化
我们可以使用行数组 \(\textit{row}\) 和列数组 \(\textit{col}\) 来记录每一行、每一列被增加的次数。对于 \(\textit{indices}\) 中的每一对 \((r_i, c_i)\),我们将 \(\textit{row}[r_i]\) 和 \(\textit{col}[c_i]\) 分别加 \(1\)。
操作结束后,可以算出 \((i, j)\) 位置的计数为 \(\textit{row}[i]+\textit{col}[j]\)。遍历矩阵,统计奇数的个数。
时间复杂度 \(O(k + m \times n)\),空间复杂度 \(O(m + n)\)。其中 \(k\) 为 \(\textit{indices}\) 的长度。
| class Solution:
def oddCells(self, m: int, n: int, indices: List[List[int]]) -> int:
row = [0] * m
col = [0] * n
for r, c in indices:
row[r] += 1
col[c] += 1
return sum((i + j) % 2 for i in row for j in col)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 | class Solution {
public int oddCells(int m, int n, int[][] indices) {
int[] row = new int[m];
int[] col = new int[n];
for (int[] e : indices) {
int r = e[0], c = e[1];
row[r]++;
col[c]++;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i : row) {
for (int j : col) {
ans += (i + j) % 2;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 | class Solution {
public:
int oddCells(int m, int n, vector<vector<int>>& indices) {
vector<int> row(m);
vector<int> col(n);
for (auto& e : indices) {
int r = e[0], c = e[1];
row[r]++;
col[c]++;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i : row) {
for (int j : col) {
ans += (i + j) % 2;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 | func oddCells(m int, n int, indices [][]int) int {
row := make([]int, m)
col := make([]int, n)
for _, e := range indices {
r, c := e[0], e[1]
row[r]++
col[c]++
}
ans := 0
for _, i := range row {
for _, j := range col {
ans += (i + j) % 2
}
}
return ans
}
|
方法三:数学优化
我们注意到,只有当 \(\textit{row}[i]\) 和 \(\textit{col}[j]\) 中恰好为“一奇一偶”时,矩阵 \((i, j)\) 位置的数才会是奇数。
我们统计 \(\textit{row}\) 中的奇数个数,记为 \(\textit{cnt1}\);而 \(\textit{col}\) 中的奇数个数,记为 \(\textit{cnt2}\)。那么最终得到的奇数个数为 \(\textit{cnt1} \times (n - \textit{cnt2}) + \textit{cnt2} \times (m - \textit{cnt1})\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(k + m + n)\),空间复杂度 \(O(m + n)\)。其中 \(k\) 为 \(\textit{indices}\) 的长度。
| class Solution:
def oddCells(self, m: int, n: int, indices: List[List[int]]) -> int:
row = [0] * m
col = [0] * n
for r, c in indices:
row[r] += 1
col[c] += 1
cnt1 = sum(v % 2 for v in row)
cnt2 = sum(v % 2 for v in col)
return cnt1 * (n - cnt2) + cnt2 * (m - cnt1)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 | class Solution {
public int oddCells(int m, int n, int[][] indices) {
int[] row = new int[m];
int[] col = new int[n];
for (int[] e : indices) {
int r = e[0], c = e[1];
row[r]++;
col[c]++;
}
int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
for (int v : row) {
cnt1 += v % 2;
}
for (int v : col) {
cnt2 += v % 2;
}
return cnt1 * (n - cnt2) + cnt2 * (m - cnt1);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20 | class Solution {
public:
int oddCells(int m, int n, vector<vector<int>>& indices) {
vector<int> row(m);
vector<int> col(n);
for (auto& e : indices) {
int r = e[0], c = e[1];
row[r]++;
col[c]++;
}
int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
for (int v : row) {
cnt1 += v % 2;
}
for (int v : col) {
cnt2 += v % 2;
}
return cnt1 * (n - cnt2) + cnt2 * (m - cnt1);
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 | func oddCells(m int, n int, indices [][]int) int {
row := make([]int, m)
col := make([]int, n)
for _, e := range indices {
r, c := e[0], e[1]
row[r]++
col[c]++
}
cnt1, cnt2 := 0, 0
for _, v := range row {
cnt1 += v % 2
}
for _, v := range col {
cnt2 += v % 2
}
return cnt1*(n-cnt2) + cnt2*(m-cnt1)
}
|