单调栈
数组
栈
链表
题目描述
给定一个长度为 n 的链表 head
对于列表中的每个节点,查找下一个 更大节点 的值。也就是说,对于每个节点,找到它旁边的第一个节点的值,这个节点的值 严格大于 它的值。
返回一个整数数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是第 i 个节点( 从1开始 )的下一个更大的节点的值。如果第 i 个节点没有下一个更大的节点,设置 answer[i] = 0 。
示例 1:
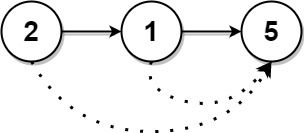
输入: head = [2,1,5]
输出: [5,5,0]
示例 2:
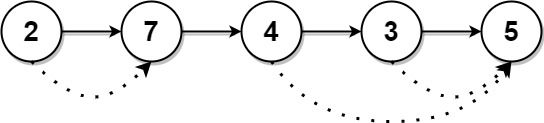
输入: head = [2,7,4,3,5]
输出: [7,0,5,5,0]
提示:
链表中节点数为 n
1 <= n <= 104 1 <= Node.val <= 109
解法
方法一:单调栈
题目要求找到链表中每个节点的下一个更大的节点,即找到链表中每个节点的右边第一个比它大的节点。我们先遍历链表,将链表中的值存入数组 \(nums\) 中。那么对于数组 \(nums\) 中的每个元素,我们只需要找到它右边第一个比它大的元素即可。求下一个更大的元素的问题可以使用单调栈来解决。
我们从后往前遍历数组 \(nums\) ,维护一个从栈底到栈顶单调递减的栈 \(stk\) ,遍历过程中,如果栈顶元素小于等于当前元素,则循环将栈顶元素出栈,直到栈顶元素大于当前元素或者栈为空。
如果此时栈为空,则说明当前元素没有下一个更大的元素,否则当前元素的下一个更大的元素就是栈顶元素,更新答案数组 \(ans\) 。然后将当前元素入栈,继续遍历。
遍历结束后,返回答案数组 \(ans\) 即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。其中 \(n\) 为链表的长度。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust JavaScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution :
def nextLargerNodes ( self , head : Optional [ ListNode ]) -> List [ int ]:
nums = []
while head :
nums . append ( head . val )
head = head . next
stk = []
n = len ( nums )
ans = [ 0 ] * n
for i in range ( n - 1 , - 1 , - 1 ):
while stk and stk [ - 1 ] <= nums [ i ]:
stk . pop ()
if stk :
ans [ i ] = stk [ - 1 ]
stk . append ( nums [ i ])
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int [] nextLargerNodes ( ListNode head ) {
List < Integer > nums = new ArrayList <> ();
for (; head != null ; head = head . next ) {
nums . add ( head . val );
}
Deque < Integer > stk = new ArrayDeque <> ();
int n = nums . size ();
int [] ans = new int [ n ] ;
for ( int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; -- i ) {
while ( ! stk . isEmpty () && stk . peek () <= nums . get ( i )) {
stk . pop ();
}
if ( ! stk . isEmpty ()) {
ans [ i ] = stk . peek ();
}
stk . push ( nums . get ( i ));
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
vector < int > nextLargerNodes ( ListNode * head ) {
vector < int > nums ;
for (; head ; head = head -> next ) {
nums . push_back ( head -> val );
}
stack < int > stk ;
int n = nums . size ();
vector < int > ans ( n );
for ( int i = n - 1 ; ~ i ; -- i ) {
while ( ! stk . empty () && stk . top () <= nums [ i ]) {
stk . pop ();
}
if ( ! stk . empty ()) {
ans [ i ] = stk . top ();
}
stk . push ( nums [ i ]);
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func nextLargerNodes ( head * ListNode ) [] int {
nums := [] int {}
for ; head != nil ; head = head . Next {
nums = append ( nums , head . Val )
}
stk := [] int {}
n := len ( nums )
ans := make ([] int , n )
for i := n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- {
for len ( stk ) > 0 && stk [ len ( stk ) - 1 ] <= nums [ i ] {
stk = stk [: len ( stk ) - 1 ]
}
if len ( stk ) > 0 {
ans [ i ] = stk [ len ( stk ) - 1 ]
}
stk = append ( stk , nums [ i ])
}
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function nextLargerNodes ( head : ListNode | null ) : number [] {
const nums : number [] = [];
while ( head ) {
nums . push ( head . val );
head = head . next ;
}
const stk : number [] = [];
const n = nums . length ;
const ans : number [] = Array ( n ). fill ( 0 );
for ( let i = n - 1 ; ~ i ; -- i ) {
while ( stk . length && stk . at ( - 1 ) ! <= nums [ i ]) {
stk . pop ();
}
ans [ i ] = stk . length ? stk . at ( - 1 ) ! : 0 ;
stk . push ( nums [ i ]);
}
return ans ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41 // Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
use std :: collections :: VecDeque ;
impl Solution {
pub fn next_larger_nodes ( head : Option < Box < ListNode >> ) -> Vec < i32 > {
let mut nums = Vec :: new ();
let mut current = & head ;
while let Some ( node ) = current {
nums . push ( node . val );
current = & node . next ;
}
let mut stk = VecDeque :: new ();
let n = nums . len ();
let mut ans = vec! [ 0 ; n ];
for i in ( 0 .. n ). rev () {
while ! stk . is_empty () && stk . back (). copied (). unwrap () <= nums [ i ] {
stk . pop_back ();
}
if let Some ( & top ) = stk . back () {
ans [ i ] = top ;
}
stk . push_back ( nums [ i ]);
}
ans
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 /**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {number[]}
*/
var nextLargerNodes = function ( head ) {
const nums = [];
while ( head ) {
nums . push ( head . val );
head = head . next ;
}
const stk = [];
const n = nums . length ;
const ans = new Array ( n ). fill ( 0 );
for ( let i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; -- i ) {
while ( stk . length && stk [ stk . length - 1 ] <= nums [ i ]) {
stk . pop ();
}
ans [ i ] = stk . length ? stk [ stk . length - 1 ] : 0 ;
stk . push ( nums [ i ]);
}
return ans ;
};