


题目描述
在一排多米诺骨牌中,tops[i] 和 bottoms[i] 分别代表第 i 个多米诺骨牌的上半部分和下半部分。(一个多米诺是两个从 1 到 6 的数字同列平铺形成的 —— 该平铺的每一半上都有一个数字。)
我们可以旋转第 i 张多米诺,使得 tops[i] 和 bottoms[i] 的值交换。
返回能使 tops 中所有值或者 bottoms 中所有值都相同的最小旋转次数。
如果无法做到,返回 -1.
示例 1:
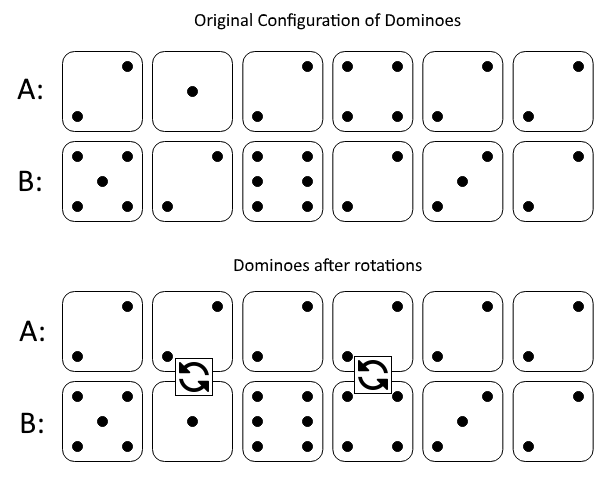
输入:tops = [2,1,2,4,2,2], bottoms = [5,2,6,2,3,2]
输出:2
解释:
图一表示:在我们旋转之前, tops 和 bottoms 给出的多米诺牌。
如果我们旋转第二个和第四个多米诺骨牌,我们可以使上面一行中的每个值都等于 2,如图二所示。
示例 2:
输入:tops = [3,5,1,2,3], bottoms = [3,6,3,3,4]
输出:-1
解释: 在这种情况下,不可能旋转多米诺牌使一行的值相等。
提示:
2 <= tops.length <= 2 * 104bottoms.length == tops.length1 <= tops[i], bottoms[i] <= 6
解法
方法一:贪心
根据题目描述,我们知道,要使得 \(tops\) 中所有值或者 \(bottoms\) 中所有值都相同,那么这个值必须是 \(tops[0]\) 或者 \(bottoms[0]\) 中的一个。
因此,我们设计一个函数 \(f(x)\),表示将所有的值都变成 \(x\) 的最小旋转次数,那么答案就是 \(\min\{f(\textit{tops}[0]), f(\textit{bottoms}[0])\}\)。
函数 \(f(x)\) 的计算方法如下:
我们用两个变量 \(cnt1\) 和 \(cnt2\) 统计 \(tops\) 和 \(bottoms\) 中等于 \(x\) 的个数,用 \(n\) 减去它们的最大值,就是将所有值都变成 \(x\) 的最小旋转次数。注意,如果 \(tops\) 和 \(bottoms\) 中没有等于 \(x\) 的值,那么 \(f(x)\) 的值就是一个很大的数,我们用 \(n + 1\) 表示这个数。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\),其中 \(n\) 是数组的长度。空间复杂度 \(O(1)\)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 | class Solution:
def minDominoRotations(self, tops: List[int], bottoms: List[int]) -> int:
def f(x: int) -> int:
cnt1 = cnt2 = 0
for a, b in zip(tops, bottoms):
if x not in (a, b):
return inf
cnt1 += a == x
cnt2 += b == x
return len(tops) - max(cnt1, cnt2)
ans = min(f(tops[0]), f(bottoms[0]))
return -1 if ans == inf else ans
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 | class Solution {
private int n;
private int[] tops;
private int[] bottoms;
public int minDominoRotations(int[] tops, int[] bottoms) {
n = tops.length;
this.tops = tops;
this.bottoms = bottoms;
int ans = Math.min(f(tops[0]), f(bottoms[0]));
return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
}
private int f(int x) {
int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (tops[i] != x && bottoms[i] != x) {
return n + 1;
}
cnt1 += tops[i] == x ? 1 : 0;
cnt2 += bottoms[i] == x ? 1 : 0;
}
return n - Math.max(cnt1, cnt2);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19 | class Solution {
public:
int minDominoRotations(vector<int>& tops, vector<int>& bottoms) {
int n = tops.size();
auto f = [&](int x) {
int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (tops[i] != x && bottoms[i] != x) {
return n + 1;
}
cnt1 += tops[i] == x;
cnt2 += bottoms[i] == x;
}
return n - max(cnt1, cnt2);
};
int ans = min(f(tops[0]), f(bottoms[0]));
return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 | func minDominoRotations(tops []int, bottoms []int) int {
n := len(tops)
f := func(x int) int {
cnt1, cnt2 := 0, 0
for i, a := range tops {
b := bottoms[i]
if a != x && b != x {
return n + 1
}
if a == x {
cnt1++
}
if b == x {
cnt2++
}
}
return n - max(cnt1, cnt2)
}
ans := min(f(tops[0]), f(bottoms[0]))
if ans > n {
return -1
}
return ans
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 | function minDominoRotations(tops: number[], bottoms: number[]): number {
const n = tops.length;
const f = (x: number): number => {
let [cnt1, cnt2] = [0, 0];
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (tops[i] !== x && bottoms[i] !== x) {
return n + 1;
}
cnt1 += tops[i] === x ? 1 : 0;
cnt2 += bottoms[i] === x ? 1 : 0;
}
return n - Math.max(cnt1, cnt2);
};
const ans = Math.min(f(tops[0]), f(bottoms[0]));
return ans > n ? -1 : ans;
}
|



